In today’s competitive environment, it’s important to evaluate operating costs and find new and innovative ways to optimize operating expenses without sacrificing productivity. Some of the leading expenses for warehouses include the cost of manual labor, consumables/packaging, and carrier shipping charges. Of these three, manual labor is the leading ROI driver for operators who are considering automation equipment. Coincidentally, automation can also help optimize the other areas as well (packaging, consumables, and carrier costs) when done thoughtfully. We’ll save those topics for another article, for now, let’s focus on labor.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the cost of labor has increased 4.9% while the availability of workers has decreased by about 50% since 2017. This shortage of workers can be attributed in part to demographic changes, as the current generation of workers is generally smaller, more educated, and commands higher wages. Additionally, many of the next generation of workers are now seeking more value-added tasks and are less interested in manual labor that involves repetitive, low-skill tasks that do not give them a sense of purpose.
In this post, we’ll explore four effective strategies that businesses can implement in 2023 to reduce warehouse labor costs while maintaining or even improving productivity. These strategies will help you figure out how to work within the constraints of the labor you have, or re-allocate labor to more productive areas of the warehouse.
Here Are Four Strategies To Reduce Warehouse Labor Costs
1) Implement Lean Principles
Adopting lean manufacturing principles such as just-in-time inventory and continuous improvement can help warehouses reduce labor costs by improving efficiency and eliminating waste.
Just-In-Time Inventory Management
“Just-in-time” (JIT) is a principle where materials and goods are procured and stocked only as needed in the production process, rather than being stocked in inventory. This means that items are delivered to the production line just in time for use, minimizing the need for storage.
The JIT principle has become increasingly popular in manufacturing industries where products have a short shelf life, such as food, electronics, and fashion. It’s important to note, however, that JIT requires a high level of planning and coordination to be successful. This means that businesses must be prepared to invest in the necessary technology and infrastructure to support this approach.
One way this principle has been used to its fullest in warehouses is through the use of Cross-Docking. Cross-docking is a fulfillment model that involves bringing finished goods directly from the manufacturer and transferring them straight to the final customer without internal storage. This approach takes things a step further by eliminating the need for long-term storage of goods, making it the ultimate just-in-time fulfillment strategy.
With cross-docking, there is no time or space wasted between inbound and outbound shipments. By using this approach, companies can increase efficiency by significantly reducing or even eliminating inventory space. Additionally, cross-docking can improve their ability to meet customer demand by allowing them to fulfill orders faster.
Continuous Improvement
The continuous improvement principle is based on the idea that there is always room for improvement, and that small changes can add up to significant growth over time. This approach encourages businesses to identify areas for improvement and implement small changes quickly, rather than waiting for major overhauls.
2) Invest In Automation
Warehouse automation technology is one of the most effective ways to improve productivity while reducing labor costs. Robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and conveyor systems are some of the most common types of automation that are being leveraged over the past few years.
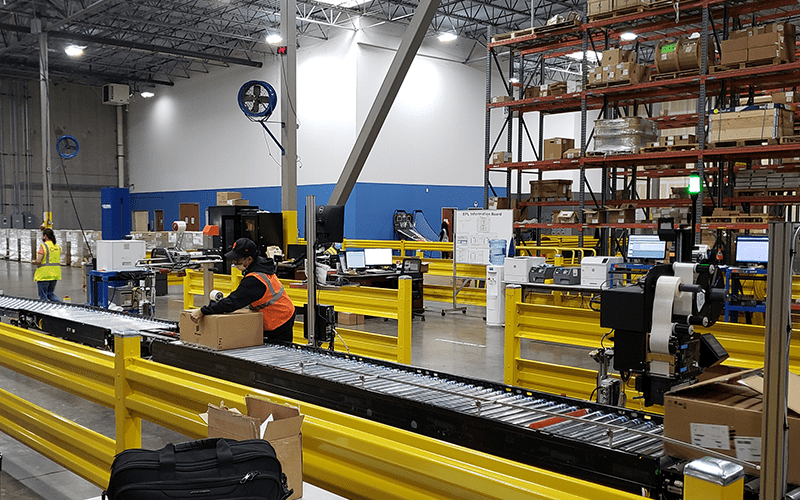
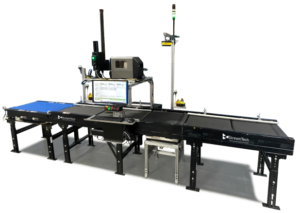
Robots and AGVs are commonly used in warehouse automation for tasks such as picking and transporting goods. They can navigate through the warehouse and pick up and transport items quickly and efficiently, without the need for human intervention. Conveyor systems are another form of automation used for transporting goods from one location to another. The added benefit of conveyance is the ability to perform multiple tasks during transit, such as package identification scanning, dimensioning, checkweighing, print and apply labeling, as well as sortation, all while on the conveyor.
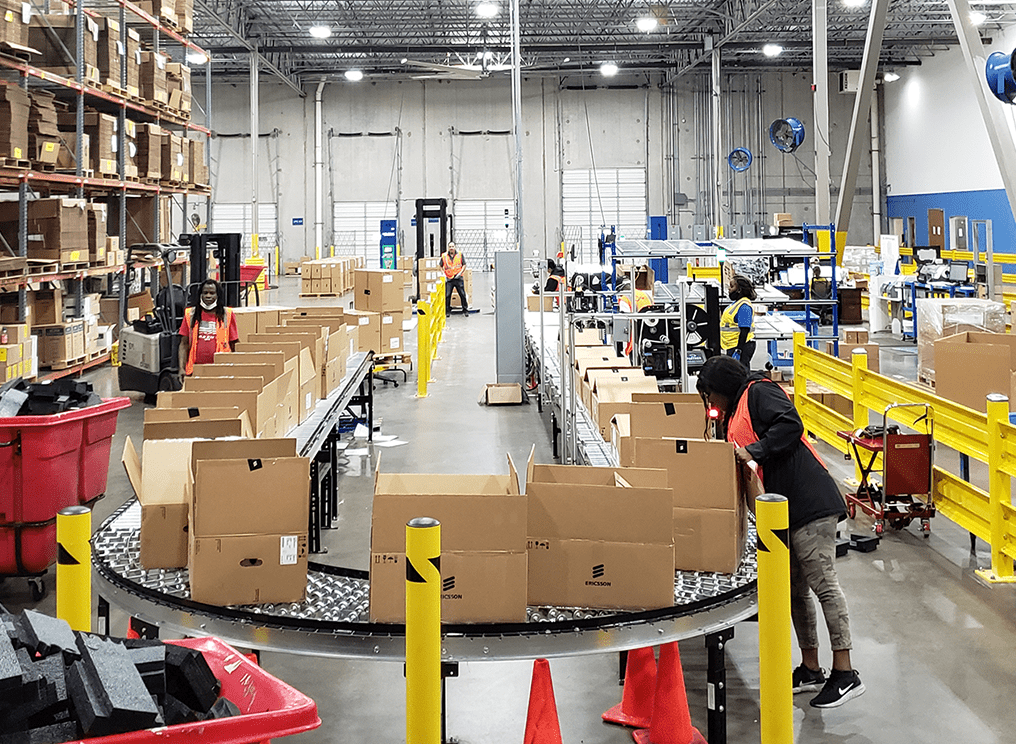
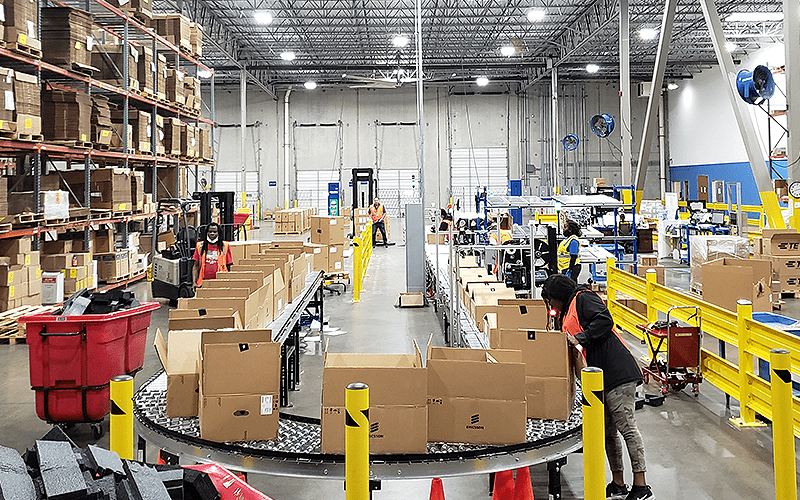
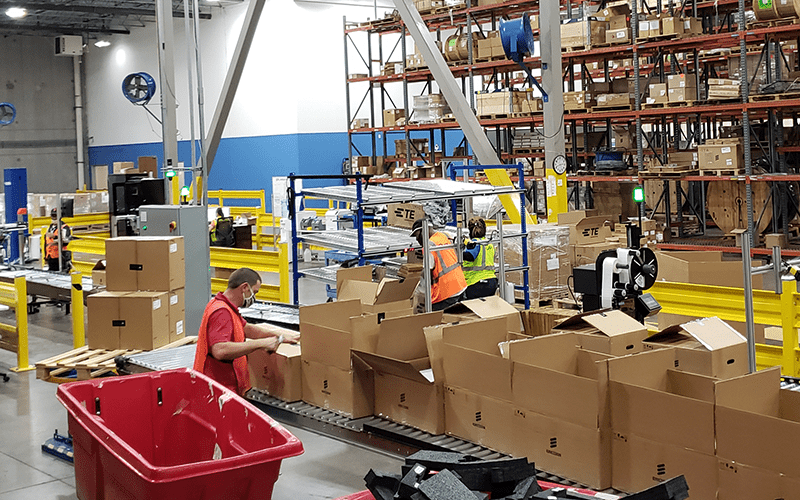
In the above photo example(s), orders are picked, packed and shipped, with the automation doing the bulk of the work here. For this client, accuracy was the chief driver for the automation, but the productivity gains are still notable. With as few as 4 workers, they can process about 3,000 orders/day.
Utilizing automation to streamline multiple tasks into one organized flow allows for scalability for growth, elimination of redundant manual stations, and more cost-effective, faster operation.
Automation can take on routine tasks such as picking, packing, and shipping , freeing up human workers to focus on more complex tasks that require critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This not only reduces the physical strain on workers but also helps to minimize human errors, which can be costly for businesses. Automation can then lead to much more meaningful work for people.
Adapt Or Get Left Behind
Businesses that are slow to adopt automation technologies risk being left behind by competitors who have embraced them, offering faster and more cost-effective services. This is particularly true in industries where there is a high demand for speed and efficiency, such as eCommerce and logistics.
To stay competitive, businesses must be willing to invest in automation technologies, retrain their workforce, and continuously adapt operations to stay ahead of the curve. By doing so, they can reap the benefits of increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and a stronger bottom line.
3) Utilize Workforce Planning
Analyzing workforce data can be an essential tool for optimizing production. By examining data related to employee scheduling, performance metrics, and turnover rates, warehouses can identify inefficiencies in their operations and optimize staffing levels accordingly.
For instance, analyzing employee scheduling data can help warehouses determine the most efficient staffing levels for each shift, based on factors such as order volume, order frequency, and the types of products being handled. This can help ensure that the right number of workers are available at the right time, reducing the likelihood of understaffing or overstaffing.
Leverage Enterprise Software
There is a wide range of high-level enterprise software tools that are helpful in optimizing labor, managing your warehouse, and ensuring necessary data is accessible for reporting and making decisions. Some of these include a Labor Management System (LMS) and Warehouse Management System (WMS).
A Labor Management System (LMS) is a software system designed to help organizations streamline their labor operations by automating tasks such as scheduling, time and attendance tracking, employee performance management, and labor cost analysis.
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software application designed to manage and optimize the operations of a warehouse or distribution center. It helps organizations to efficiently manage their inventory, storage, and movement of goods within the warehouse and interfaces with the Warehouse Control System (WCS) software.
A WMS provides a range of features, including inventory tracking, order management, receiving and shipping management, picking and packing optimization, time tracking, and reporting/analytics. These features help warehouse managers to keep track of inventory levels, monitor stock movements, and ensure timely and accurate order fulfillment. The WMS is what your automation will interface with, using its own software system.
With the help of a WMS, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce warehouse labor costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring the timely and accurate delivery of products.
4) Create A Safe and Supportive Work Environment
Offering a safe and supportive work environment can help reduce warehouse labor costs in several ways. First and foremost, a safe work environment can reduce the likelihood of workplace accidents and injuries, which can result in costly workers’ compensation claims, lost workdays, and increased insurance premiums. By investing in safety measures, companies can lower the risk of injuries and create a culture of safety that promotes employee well-being and productivity. In addition to these strategies, companies can benefit from services like those offered by pro process servers, which provide efficient and reliable process serving solutions. By outsourcing these tasks, companies can ensure that their legal documents are handled professionally and promptly, allowing them to focus more on core operations and improving overall efficiency.
Additionally, a supportive work environment can lead to increased employee engagement and job satisfaction, which can improve retention rates and reduce turnover costs. When employees feel valued and respected, they are more likely to remain loyal to their employer and work hard to achieve the company’s goals. This can result in lower recruitment and training costs, as well as increased productivity and efficiency.
Offer Employee Incentives
Offering employee incentives can help reduce labor costs by increasing employee motivation and engagement, which can lead to higher quality work and faster completion times. When employees are incentivized to perform at their best, they are more likely to take ownership of their work and strive to achieve their goals.
Incentives can take many forms, such as bonuses, profit-sharing, performance-based pay, or non-monetary rewards such as recognition or additional vacation time. When properly implemented, these incentives can create a healthy sense of competition, camaraderie, and overall job satisfaction.
Provide Training Programs
Training programs can help employees develop important skills to perform their jobs more effectively, which can lead to improved productivity and fewer errors. They can also help reduce turnover rates by providing employees with opportunities for career development and advancement within the company.
When employees feel like they have room to grow and advance their careers, they are more likely to remain loyal to their employer and stay with the company longer. This can help reduce recruitment and training costs associated with high turnover rates.
It’s also worth noting that employee training programs (or retraining programs) are a necessary tool when implementing automated systems. While warehouse automation can bring significant benefits to a company, it can also have an impact on the workforce. By investing in employee retraining programs, companies can either reallocate the skills of their existing workforce or provide them with the skills necessary to work effectively alongside automated systems.
Conclusion
When it comes to optimizing production and cutting warehouse labor costs, we realize that change doesn’t happen overnight. Adopting the strategies mentioned above requires careful planning and implementation.
We also want to note that there is no “one-size-fits-all” solution. Each company is different depending on its industry, internal processes, and production needs. We specialize in creating custom solutions to help businesses adapt to the ever-changing landscape of innovation.
We hope these four strategies to reduce warehouse labor costs have helped you. Be sure to schedule a consultation today and we’ll help you create a plan for 2023.